Explorative projects:
- Generation of novel COX-2 selective activity probes
- Generation of coumarin-based probes
Peptide Endo-cannabinoids
About hemopressins and pepcans
Hemopressins ((x)-PVNFKLLSH) or peptide endocannabinoids (pepcans) can bind to cannabinoid receptors. RVD-hemopressin (pepcan-12) was shown to act as endogenous allosteric modulator of cannabinoid receptors, with opposite effects on CB1 and CB2, respectively. Moreover, the N-terminally elongated pepcan-23 was detected in different tissues and is postulated to be the pro-peptide of RVD-hemopressin. We are generating a conditional polypoint pepcan-12 (pro-peptide pepcan-23) specific conditional knock-in mouse strain to investigate the role of these peptides in physiology.
Papers
- Identification and quantification of a new family of peptide endocannabinoids (Pepcans) showing negative allosteric modulation at CB1 receptors. Bauer M, Chicca A, Tamborrini M, Eisen D, Lerner R, Lutz B, Poetz O, Pluschke G, Gertsch J. J Biol Chem. 2012, 287(44):36944-67.
- Localization and production of peptide endocannabinoids in the rodent CNS and adrenal medulla. Hofer SC, Ralvenius WT, Gachet MS, Fritschy JM, Zeilhofer HU, Gertsch J. Neuropharmacology. 2015, 98:78-89.
- Pepcan-12 (RVD-hemopressin) is a CB2 receptor positive allosteric modulator constitutively secreted by adrenals and in liver upon tissue damage. Petrucci V, Chicca A, Glasmacher S, Paloczi J, Cao Z, Pacher P, Gertsch J. Sci Rep. 2017, 7(1):9560.
- Characterization of pepcan-23 as pro-peptide of RVD-hemopressin (pepcan-12) and stability of hemopressins in mice. Glasmacher S & Gertsch J. Adv Biol Reg, 2021,80:100808.
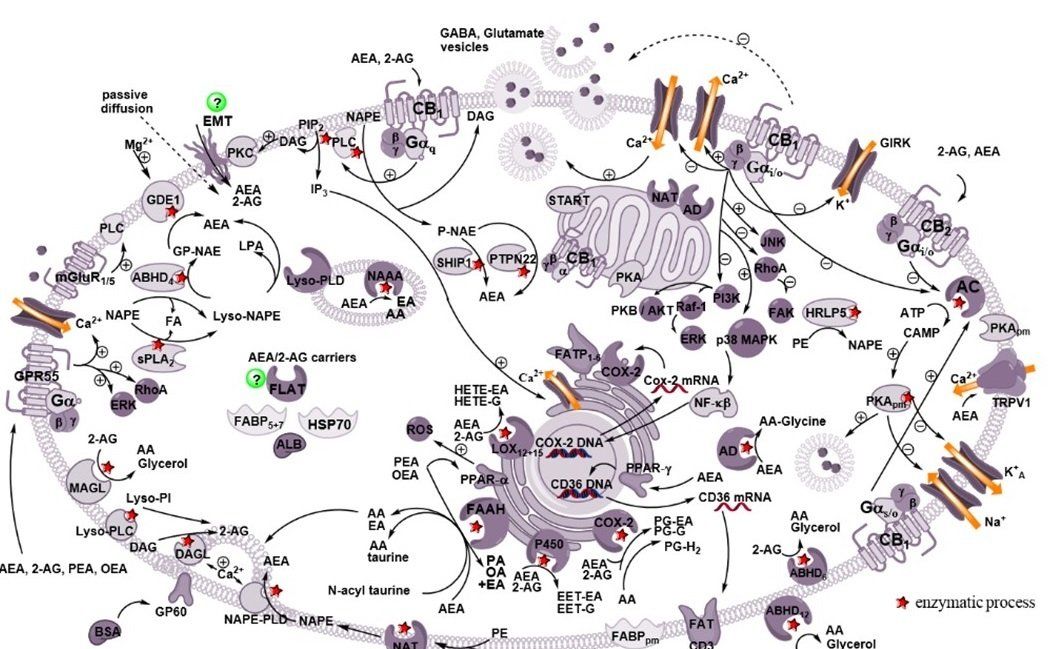
Endocannabinoid Membrane Transport
From chemical tools to targets
The extracellular effects of the endocannabinoids anandamide and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol are terminated by enzymatic hydrolysis after crossing cellular membranes by facilitated diffusion. The lack of potent and selective inhibitors for endocannabinoid transport has prevented the molecular characterization of this process, thus hindering its biochemical investigation and pharmacological exploitation. Over the last 10 years, we have generated potent and specific inhibitors to block endocannabinoid membrane transport and recently identified a novel biochemical mechanism underlying endocannabinoid reuptake.
Papers
- Selective endocannabinoid reuptake inhibitor WOBE437 reduces disease progression in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Reynoso Moreno I., Tietz S, Vallini E, Engelhardt B, Gertsch J, Chicca A. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, 2021.4(2):765-779.
- Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Endocannabinoid Uptake Inhibitors Derived from WOBE437. Mäder P, Bartholomäus R, Nicolussi S, Baumann A, Weis M, Chicca A, Rau M, Simão AC, Gertsch J, Altmann KH. ChemMedChem. 2021, 16(1):145-154.
- The Endocannabinoid Reuptake Inhibitor WOBE437 Is Orally Bioavailable and Exerts Indirect Polypharmacological Effects via Different Endocannabinoid Receptors. Reynoso-Moreno I, Chicca A, Flores-Soto ME, Viveros-Paredes JM, Gertsch J. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018, 11:180.
- Chemical probes to potently and selectively inhibit endocannabinoid cellular reuptake. Chicca A, Nicolussi S, Bartholomäus R, Blunder M, Aparisi Rey A, Petrucci V, Reynoso-Moreno IDC, Viveros-Paredes JM, Dalghi Gens M, Lutz B, Schiöth HB, Soeberdt M, Abels C, Charles RP, Altmann KH, Gertsch J. PNAS, 2017, 114(25):E5006-E5015. .
- Guineensine is a novel inhibitor of endocannabinoid uptake showing cannabimimetic behavioral effects in BALB/c mice. Nicolussi S, Viveros-Paredes JM, Gachet MS, Rau M, Flores-Soto ME, Blunder M, Gertsch J. Pharmacol Res. 2014, 80:52-65
- Evidence for bidirectional endocannabinoid transport across cell membranes. Chicca A, Marazzi J, Nicolussi S, Gertsch J. J Biol Chem. 2012, 287(41):34660-82.
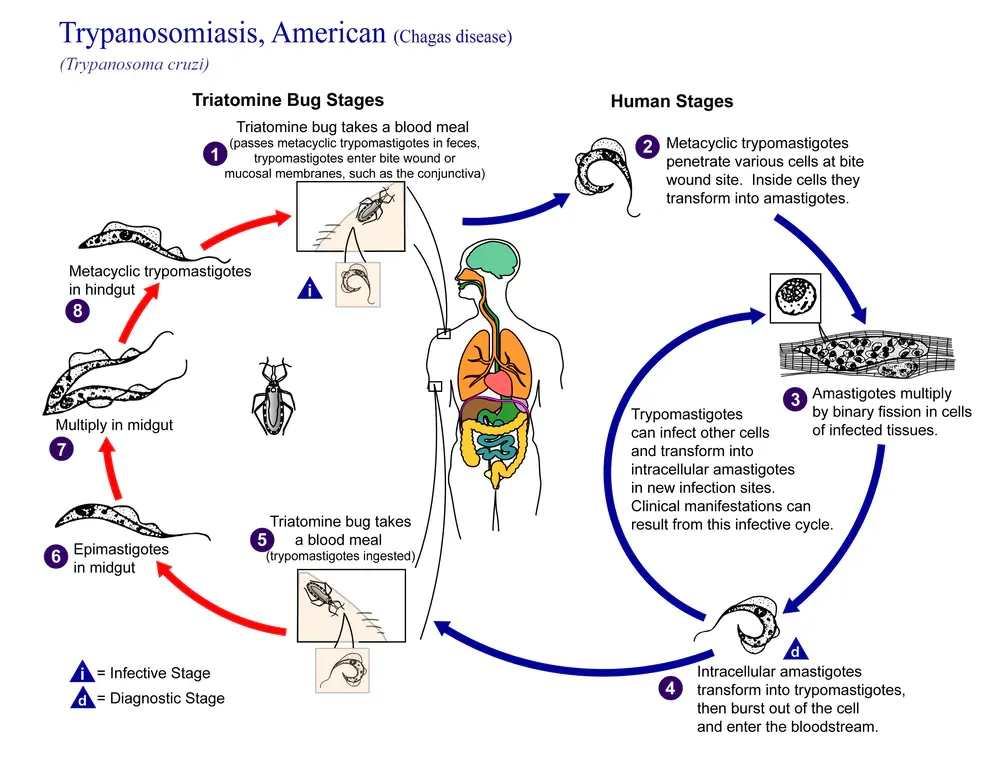
Chagas Disease
Ethnopharma-cological Fieldwork Bolivia
Chagas disease remains a major public health risk in Bolivia, particularly among rural indigenous communities. In an EU project we studied the cultural perception of the triatomine vectors and Chagas disease and the botanical drugs used in to treat symptoms among selected rural and urban ethnic groups from different socio-economic and geographical milieus. We focused on the indigenous communities in the Bolivian Chaco where the disease is hyperendemic. We study the T. cruzi infection cycle in vitro to elucidate new targets, employing the CRISPR/Cas technology and metabolomics. We are interested in how T. cruzi affects the endocannabinoid system in the host cell and whether the underlying biochemical interrelation may be exploited as new antichagasic therapeutic strategy.
Papers
- Cultural perception of triatomine bugs and Chagas disease in Bolivia: a cross-sectional field study. Salm A, Gertsch J. Parasit Vectors.12, 291.
- Phylobioactive hotspots in plant resources used to treat Chagas disease. Salm A. Krishnan RS, et al. iScience,24(4):102310.
- Semisynthetic Ecdysteroid Cinnamate Esters and tert-Butyl Oxime Ether Derivatives with Trypanocidal Activity. Háznagy MB et al. J Nat Prod. 2024, 87, 2478-2486.
- Bioactivity-guided isolation of trypanocidal coumarins and dihydro-pyranochromones from selected Apiaceae plant species. Krishnan et al. Phytochemistry. 2023, 213:113770.
SLC7 Amino Acid Transport
Generation of LAT1 inhibitors
Absence, overexpression or malfunctioning of the amino acid transporter LAT1 is associated with human diseases, in particular tumor growth. Cancer cells have reprogramed their energy metabolism to efficiently support tumor growth and metastasis formation. This includes alterations of amino acid catabolism and upregulation of amino acid transporters that lead to the activation of crucial signalling pathways, e.g. mTOR, linking growth signals to nutrient availability.
Papers
- The LAT1 inhibitor JPH203 reduces growth of thyroid carcinoma in a fully immunocompetent mouse model. Häfliger P, Graff J, Rubin M, Stooss A, Dettmer MS, Altmann KH, Gertsch J, Charles RP. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018, 37(1):234.
- Small molecule inhibitors provide insights into the relevance of LAT1 and LAT2 in materno-foetal amino acid transport. Zaugg J, Huang X, Ziegler F, Rubin M, Graff J, Müller J, Moser-Hässig R, Powell T, Gertsch J, Altmann KH, Albrecht C. J Cell Mol Med. 24(21):12681-12693
- Mechanism of substrate transport and inhibition of the human LAT1-4F2hc amino acid transporter Yan R., Li Y., Müller J, Zhang Y, Singer S, Zhong X, Gertsch J, Altmann KH, Zhou Q. Cell Discov 7(1):16
Targeted Metabolomics
LC-MS/MS
Targeted metabolomics is a quantitative approach where a specific group of metabolites are quantified with the help of internal or external standards using LC-MS/MS. We are specialized on both endogenous molecules (lipids, amino acids and neurotransmitters) as well as xenobiotics (context of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics).
Papers
- Juniperonic Acid Biosynthesis is Essential in Caenorhabditis Elegans Lacking Δ6 Desaturase (fat-3) and Generates New ω-3 Endocannabinoids. Guha S, Calarco S, Gachet MS, Gertsch J. Cells. 2020, 9(9):2127.
- Effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate on neurophysiological correlates of performance and conflict monitoring. Dornbierer DA, Kometer M, Von Rotz R, Studerus E, Gertsch J, Gachet MS, Vollenweider FX, Seifritz E, Bosch OG, Quednow BB. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29(4):539-548.
- Targeted metabolomics shows plasticity in the evolution of signaling lipids and uncovers old and new endocannabinoids in the plant kingdom. Gachet MS, Schubert A, Calarco S, Boccard J, Gertsch J. Sci Rep. 2017, 7:41177.
- Quantitative analysis of arachidonic acid, endo-cannabinoids, N-acylethanolamines and steroids in biological samples by LCMS/MS: Fit to purpose. Gachet MS, Gertsch J. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016, 1012-1013:215-21.
- 4'-O-methylhonokiol increases levels of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol in mouse brain via selective inhibition of its COX-2-mediated oxygenation. Chicca A, Gachet MS, Petrucci V, Schuehly W, Charles RP, Gertsch J. J Neuroinflammation. 2015, 12:89.
- Gamma-hydroxybutyrate enhances mood and prosocial behavior without affecting plasma oxytocin and testosterone. Bosch OG, Eisenegger C, Gertsch J, von Rotz R, Dornbierer D, Gachet MS, Heinrichs M, Wetter TC, Seifritz E, Quednow BB. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015, 62:1-10.
- A quantitiative LC-MS/MS method for the measurement of arachidonic acid, prostanoids, endocannabinoids, N-acylethanolamines and steroids in human plasma. Gachet MS, Rhyn P, Bosch OG, Quednow BB, Gertsch J. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015, 976-977:6-18.
Medical Cannabis
Cannabimimetics
The botanical drug cannabis flos (inflorescence of Cannabis sativa L.) has a unique popular status as being a potent rec-reational drug and bona fide universal remedy (panacea). Generally, cannabinoids exert therapeutic effects in a broad range of pathophysiologies related to inflammation, pain, metabolic and stress-related conditions in preclinical animal models. However, the translation of such data to humans still lacks an evidence-based foundation. We are interested in the link between secondary metabolites in food and modulation of the endocannabinoid system.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a major lipid signalling network that plays important pro-homeostatic (allostatic) roles not only in the nervous system but also in peripheral organs. There is increasing evidence that there is a dietary component in the modulation of the ECS. Cannabinoid receptors in hominids co-evolved with diet, and the ECS constitutes a feedback loop for food selection and energy metabolism. Dietary secondary metabolites from vegetables and spices able to enhance the activity of cannabinoid-type 2 (CB2 ) receptors may provide adaptive metabolic advantages and counteract inflammation. In contrast, chronic CB1 receptor activation in hedonic obese individuals may enhance pathophysiological processes related to hyperlipidaemia, diabetes, hepatorenal inflammation and cardiometabolic risk. Food able to modulate the CB1 /CB2 receptor activation ratio may thus play a role in the nutrition transition of Western high-calorie diets.
Selected Papers
- Uncovering the psychoactivity of a cannabinoid from liverworts associated with a legal high. Chicca A, Schafroth MA, Reynoso-Moreno I, Erni R, Petrucci V, Carreira EM, Gertsch J. Sci Adv. 2018, 4(10):eaat2166.
- The Intricate Influence of the Placebo Effect on Medical Cannabis and Cannabinoids. Gertsch J. Med Cannabis Cannabinoids 2018;1:60–64
- Cannabimimetic phytochemicals in the diet - an evolutionary link to food selection and metabolic stress adaptation? Gertsch J.Br J Pharmacol. 2017, 174(11):1464-1483.
- Phytocannabinoids beyond the Cannabis plant - do they exist? Gertsch J, Pertwee RG, Di Marzo V. Br J Pharmacol. 2010, 160(3):523-9.
- Guineensine is a novel inhibitor of endocannabinoid uptake showing cannabimimetic behavioral effects in BALB/c mice. Nicolussi S, Viveros-Paredes JM, Gachet MS, Rau M, Flores-Soto ME, Blunder M, Gertsch J. Pharmacol Res. 2014, 80:52-65.
- Total Synthesis of the Endocannabinoid Uptake Inhibitor Guineensine and SAR Studies. Bartholomäus R, Nicolussi S, Baumann A, Rau M, Simão AC, Gertsch J, Altmann KH. ChemMedChem. 2019, 14(17):1590-1596.
- Correlating FAAH and anandamide cellular uptake inhibition using N-alkylcarbamate inhibitors: from ultrapotent to hyperpotent. Nicolussi S, Chicca A, Rau M, Rihs S, Soeberdt M, Abels C, Gertsch J. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014, 92(4):669-89.
- Methylhonokiol attenuates neuroinflammation: a role for cannabinoid receptors? Gertsch J, Anavi-Goffer S. J Neuroinflammation. 2012, 9:135.
- Falcarinol is a covalent cannabinoid CB1 receptor ant-agonist and induces pro-allergic effects in skin. Leonti M, Casu L, Raduner S, Cottiglia F, Floris C, Altmann KH, Gertsch J. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1815-26.
- Mechanisms of osteoclastogenesis inhibition by a novel class of biphenyl-type cannabinoid CB(2) receptor inverse agonists. Schuehly W, Paredes JM, Kleyer J, Huefner A, Anavi-Goffer S, Raduner S, Altmann KH, Gertsch J. Chem Biol. 2011, 18(8):1053-64.
- 4'-O-methylhonokiol increases levels of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol in mouse brain via selective inhibition of its COX-2-mediated oxygenation. Chicca A, Gachet MS, Petrucci V, Schuehly W, Charles RP, Gertsch J. J Neuroinflammation. 2015, 12:89.
- The antinociceptive triterpene β-amyrin inhibits 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) hydrolysis without directly targeting cannabinoid receptors. Chicca A, Marazzi J, Gertsch J. Br J Pharmacol. 2012, 167(8):1596-608.
- An Endocannabinoid Uptake Inhibitor from Black Pepper Exerts Pronounced Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Mice. Reynoso-Moreno I, Najar-Guerrero I, Escareño N, Flores-Soto ME, Gertsch J, Viveros-Paredes JM. J Agric Food Chem. 2017, 65(43):9435-9442.
- LC-HRMS/MS-based phytochemical profiling of Piper spices: Global association of piperamides with endocannabinoid system modulation. Luca VS, Minceva M, Gertsch J, Skalicka-Wozniak K. Food Research International, 2021, 141, 110123.